This post is an introduction to the EML[Entity Manipulation Language] in RAP ABAP. The examples are considered with the demo flight information.
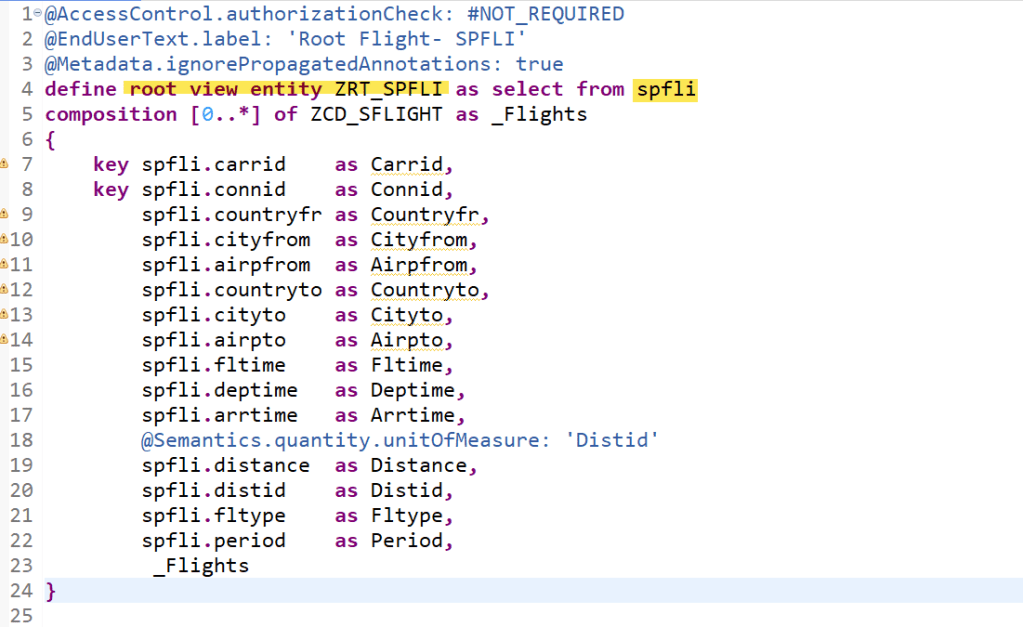
To start with- we have the below root view entity created on table SPFLI.
This is the child view entity on table SFLIGHT and having parent association to the ROOT.

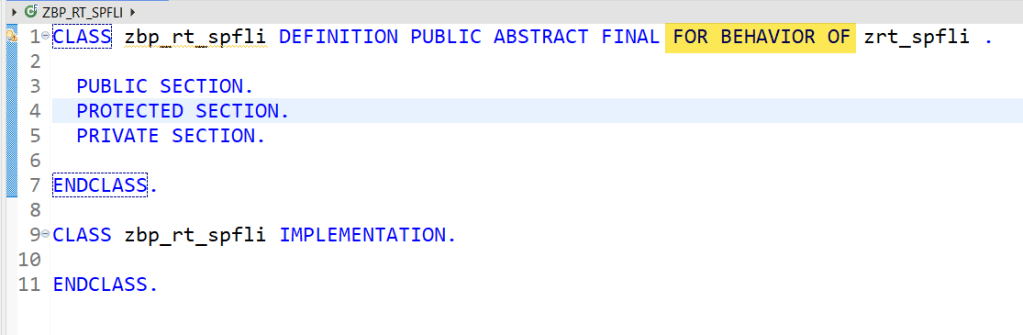
To keep it simple at start, we have 2 view entities. Now below is the behaviour definition for the root entity. The CRUD is enabled for the root and chile entity.

It is a managed scenario with the Behaviour Implementation class . Create this class in SE24 as below. As of now the class doesn’t contain any method as such.
So we are ready with our simple objects like behaviour definition and view entities to test the EML.
To learn and understand the EML on the Behv Defn and the entities, just created a simple report.
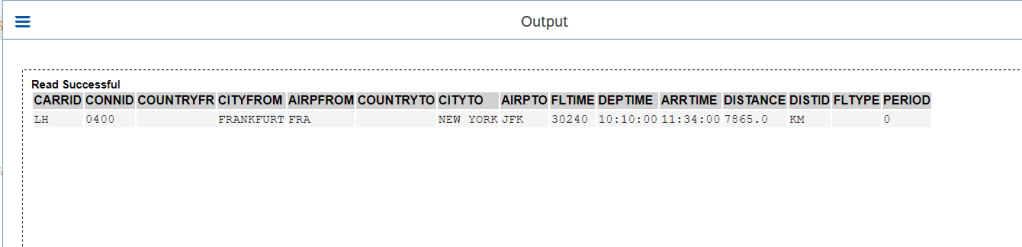
The below is a Key READ EML on the Behaviour Definition Root Entity with target for the result and for the failed read.

Once we execute the report the RESULT is populated and displayed below.
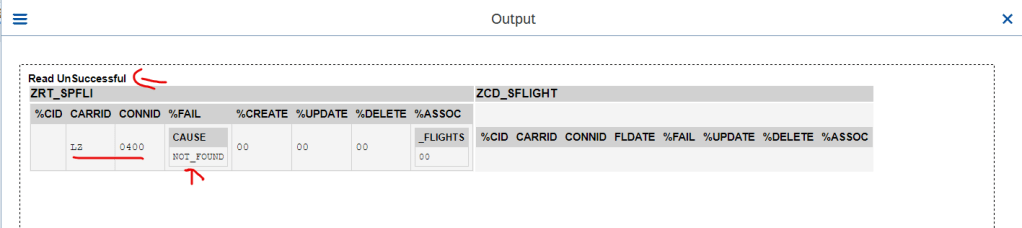
What if the information not found for the supplied key, then the read EML fills the failed target.

Read is failed and here is the output.
Above we just read the Root Entity of the Behv Definition. Now let’s check how to read the child entity or the association.

There are 2 EML read instructions- 1st is for the root entity and the 2nd is for the associated entity.
O/P-1
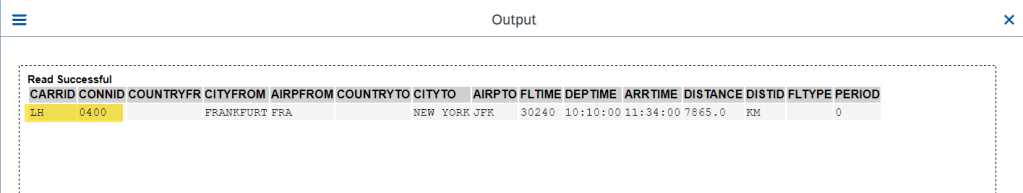
O/P-2
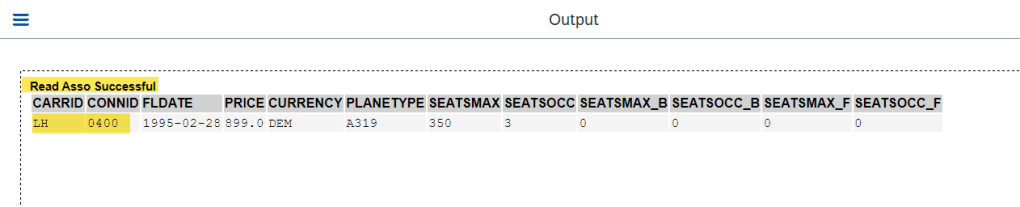
We have to specify the full key as input value for the read with READ ENTITIES statement.

O/P-1-
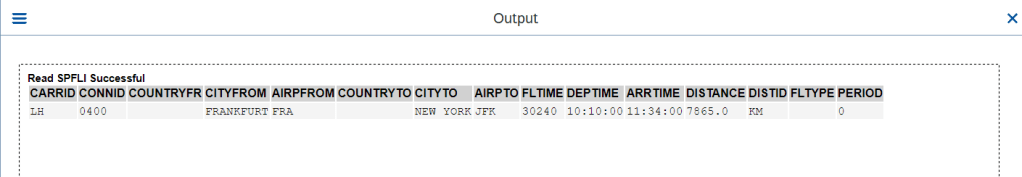
O/P-2
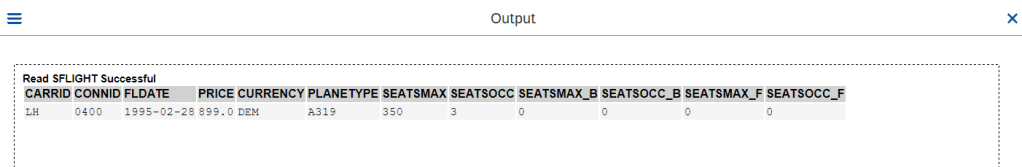
Additionally FAILED phrase can be added to collect the KEYs for which read has failed.
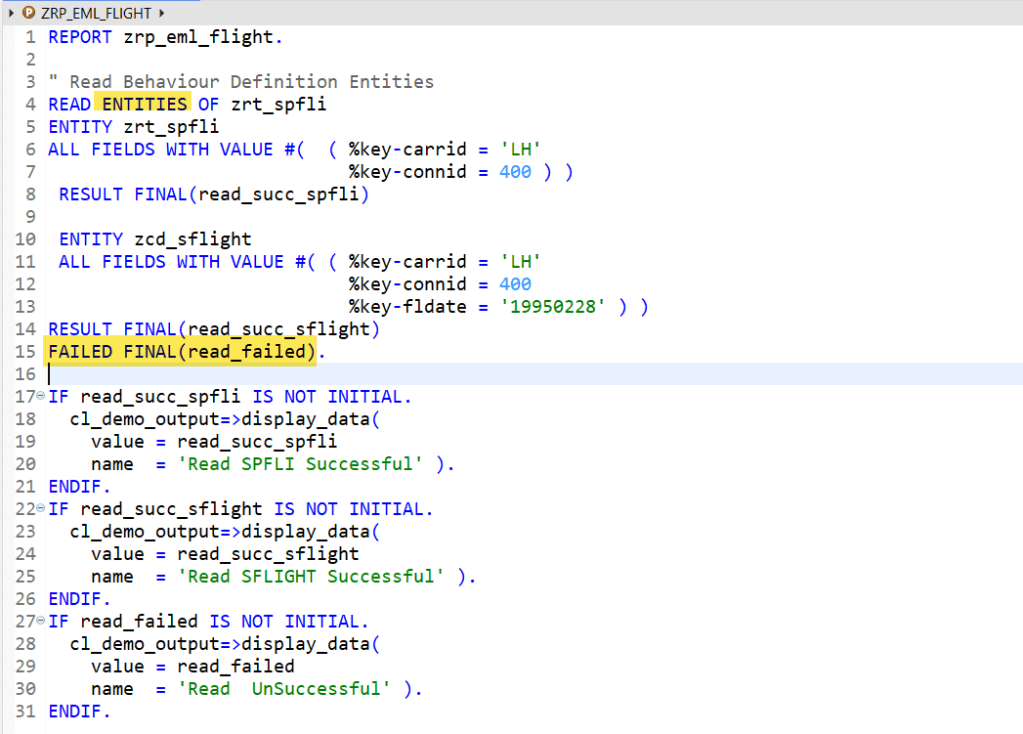
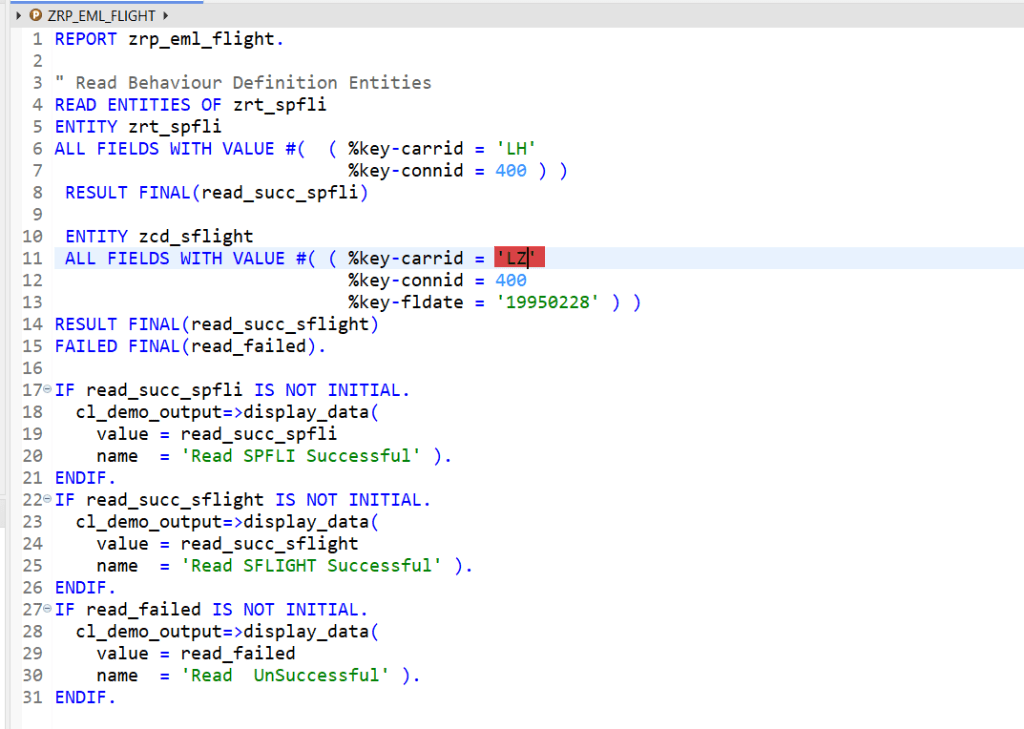
Association Entity with Failed KEY-
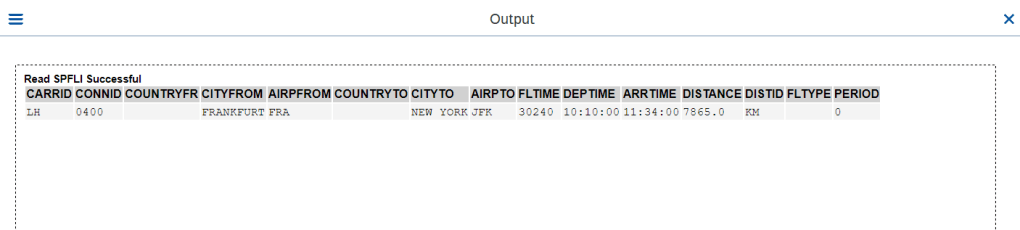
O/P-
O/P-
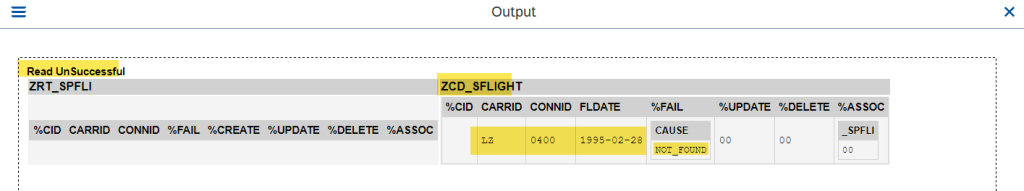
Both Entity with Failed Keys-
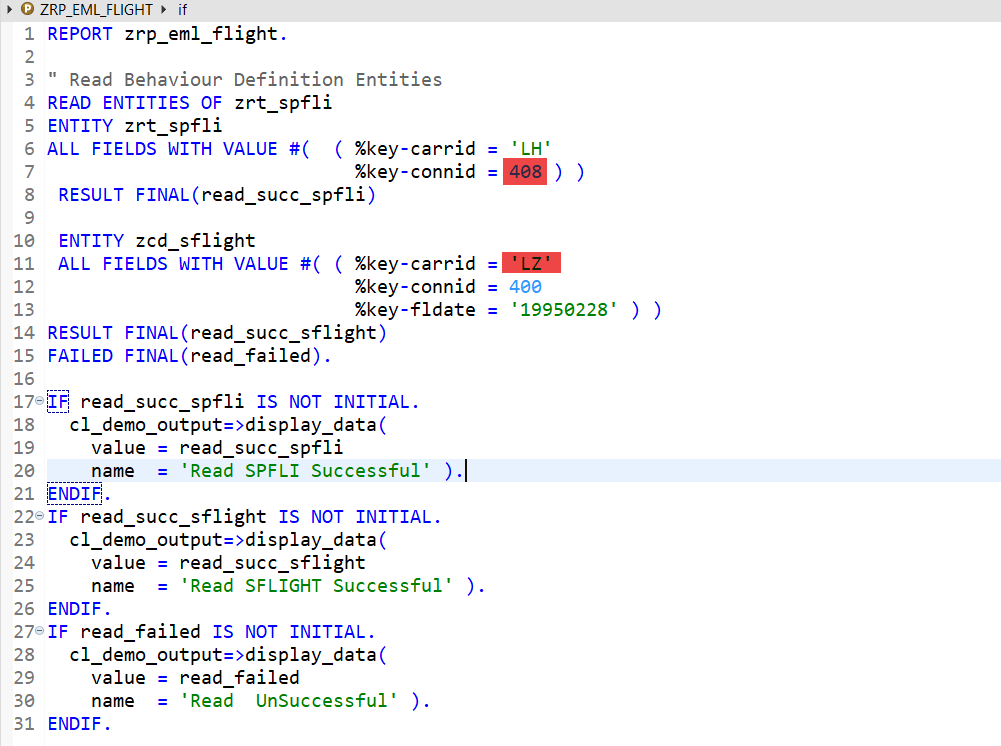
O/P-
Now next is the Read Entities with Operations-
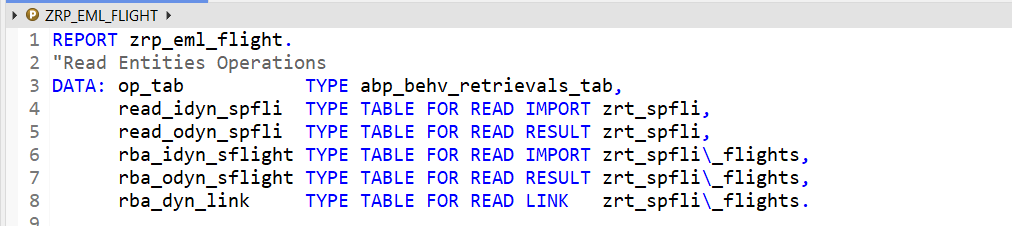
We have few data declaration for read input as import and read output as result and finally the link.
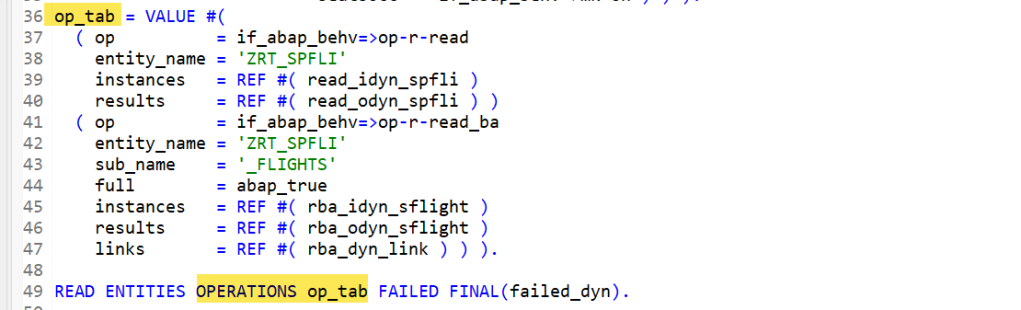
Dynamic input for Root Entity and read by association input for child entity-

Finally fill the Operation Table with input data internal table and the target result tables with link table. When the statement READ ENTITIES OPERATIONS instruction is executed, the target result table and link table are filled with relevant data.
Here we display them.

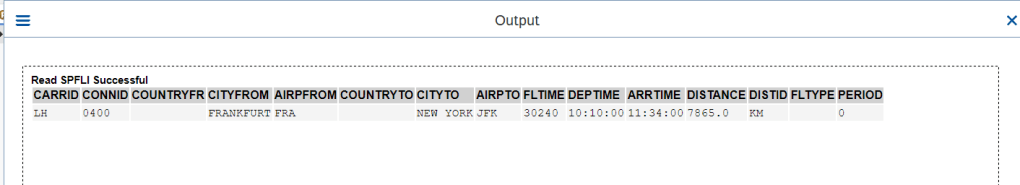
O/P- Root Entity
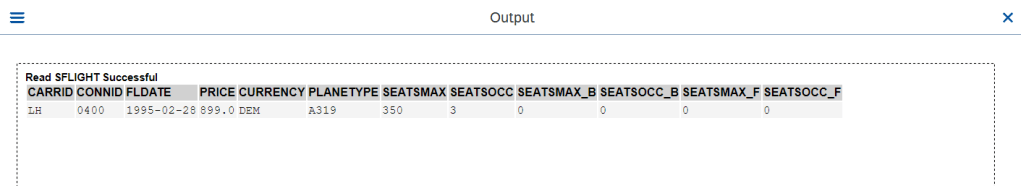
O/P- Child Entity
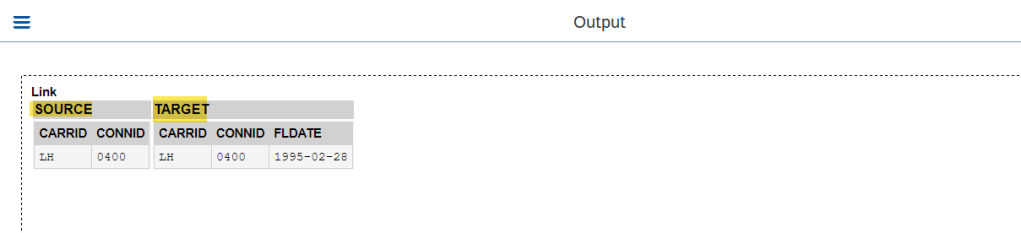
O/P- Link
Below is the EML read with specified control parameters.

O/P-
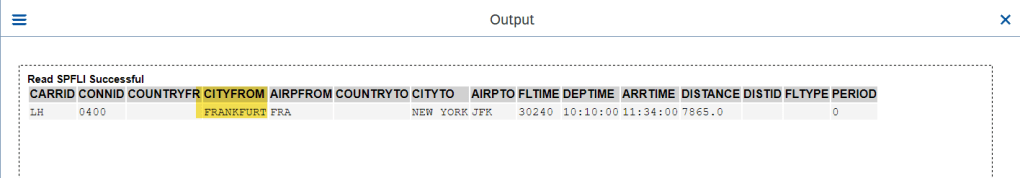
In control parameter- set specific fields to OFF and that information is not read. This is more like reading specific fields but not all.
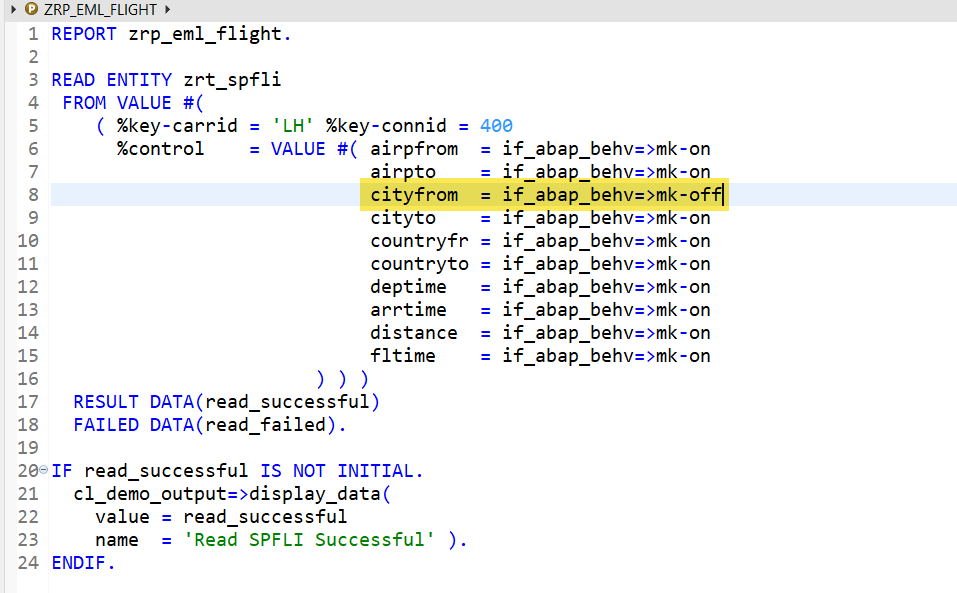
O/P-
Another READ EML where specific fields to be read can be mentioned and value input can be provided along ‘WITH’.
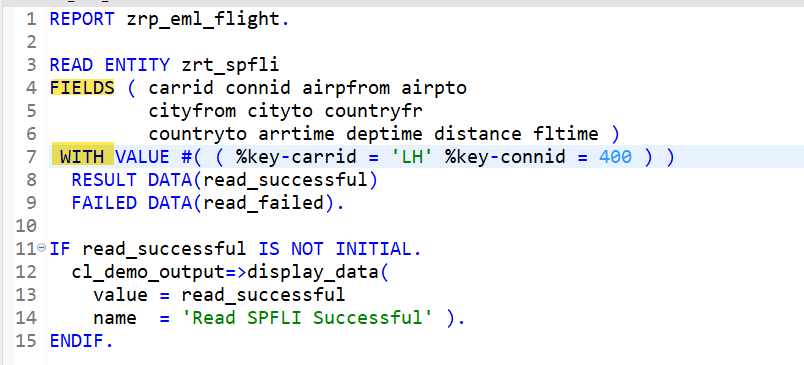
O/P-
This is a variation to read ALL Fields-
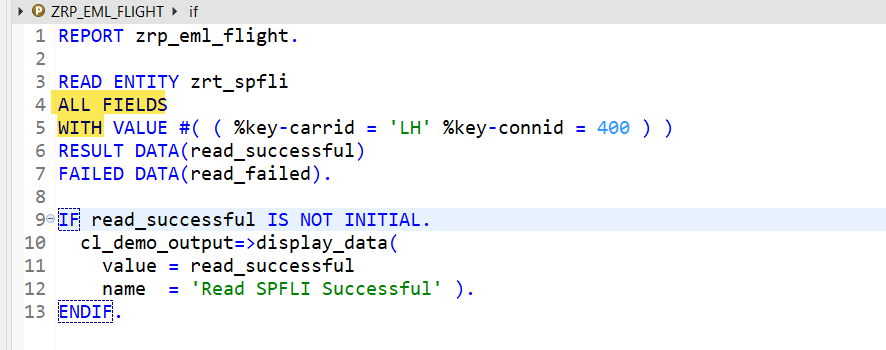
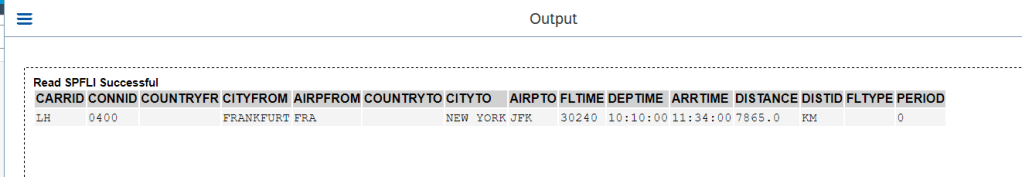
O/P-
Reading EML Child Entity with ALL Field with WITH addition-
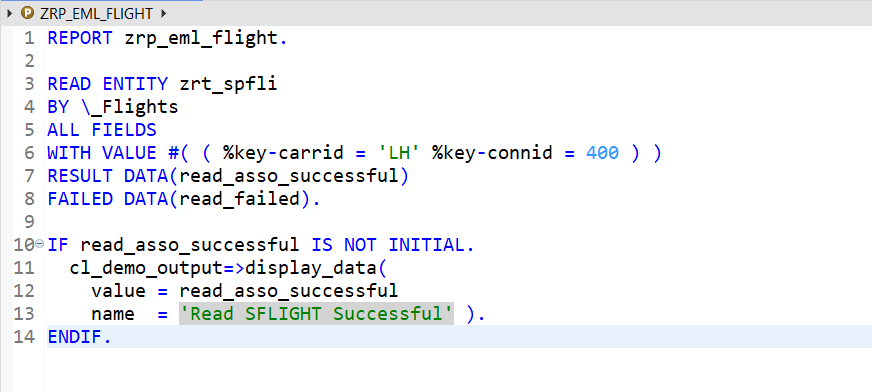
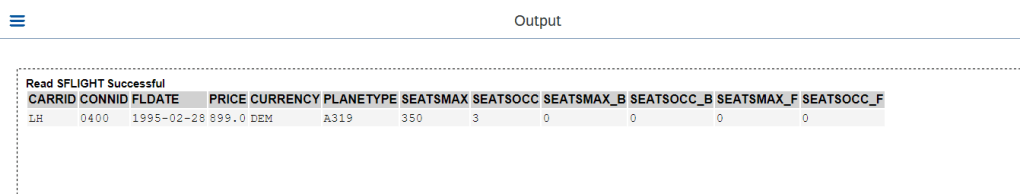
O/P-
Read with Explicit Declarations-
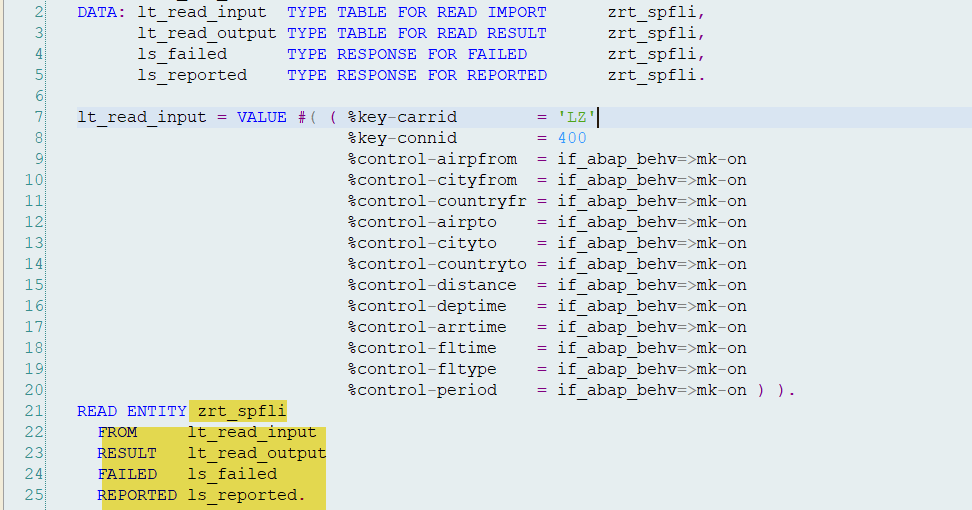
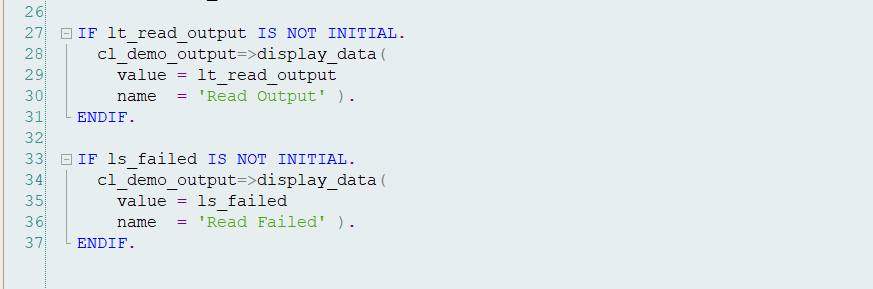
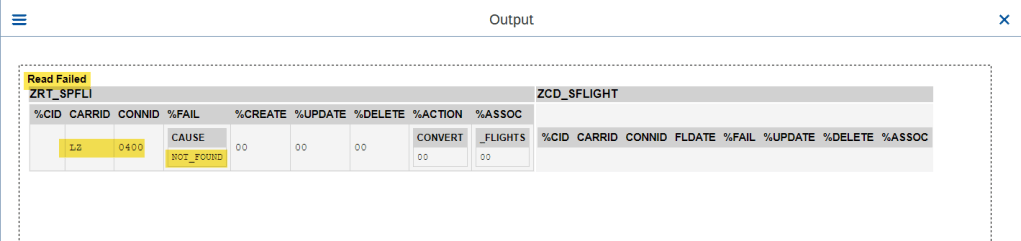
O/P1- Read Failed.
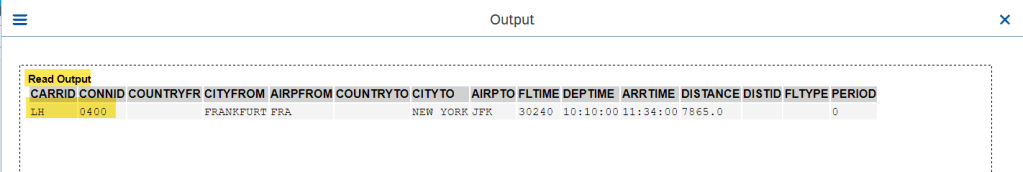
O/P2- Read Successful.
Now Let’s understand the use of FUNCTION in behavior definition. A function is typically an action that has some input and o/p result and that perform some thing on the underlying BO. Here to start with the below FUNCTION just converts the distance unit and performs a EML Read inside it.
As highlighted below- Action can be added.

Now in the Behaviour Implementation class-
Let’s define a local class that is inherited from the Behaviour Handler super class. [ There are two classes provided by the RAP framework- 1st is the behavior handler class and 2nd is the saver class] Will discuss about the saver class during the modify operation.
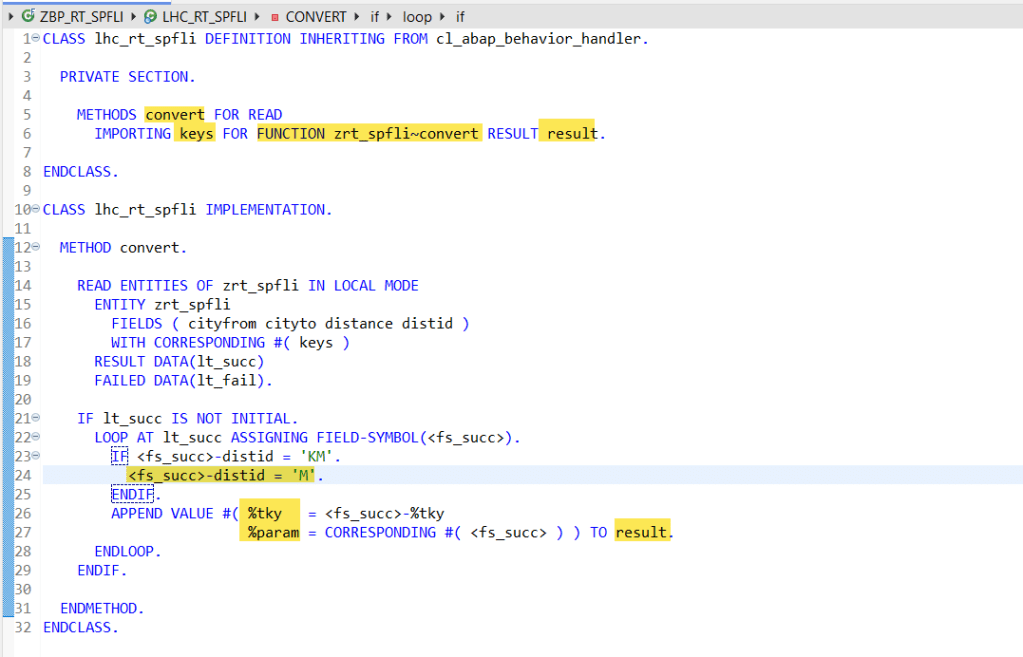
So in the local behavior handler class- define a method for the function with import and result parameters and implement this method. So this function->method just reads the root entity with the supplied KEYs and can perform some action[ in this case just converts the distance unit ] and fills the result parameter.
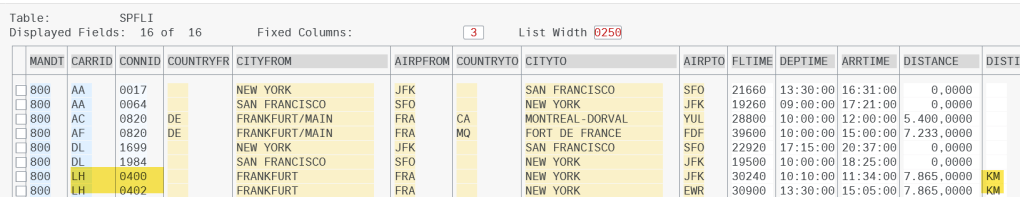
Here is the backend table.
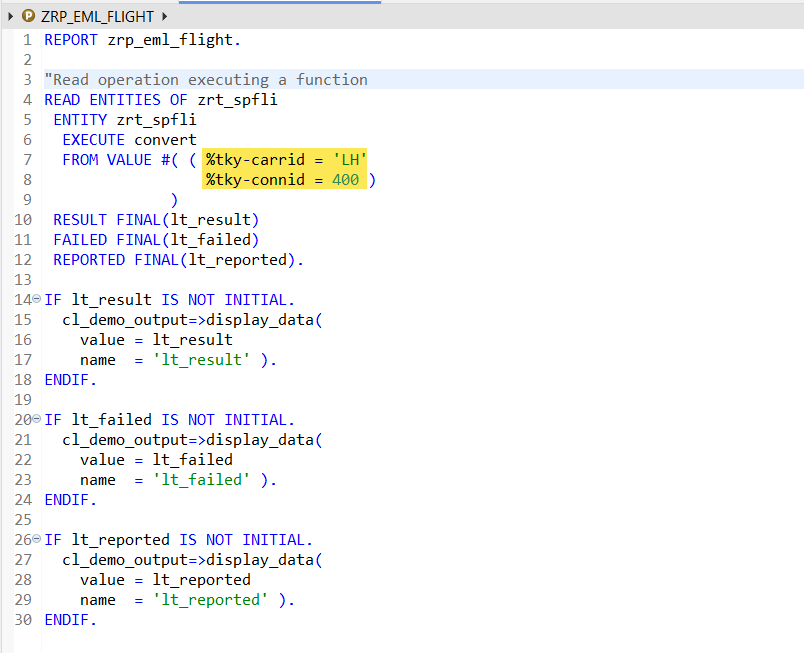
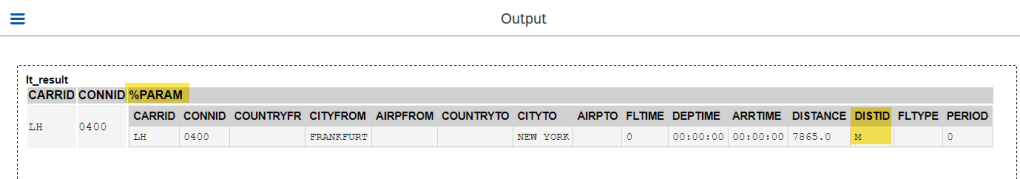
Now in the report- with READ EML execute the action- Convert and provide the input key information.
O/P-
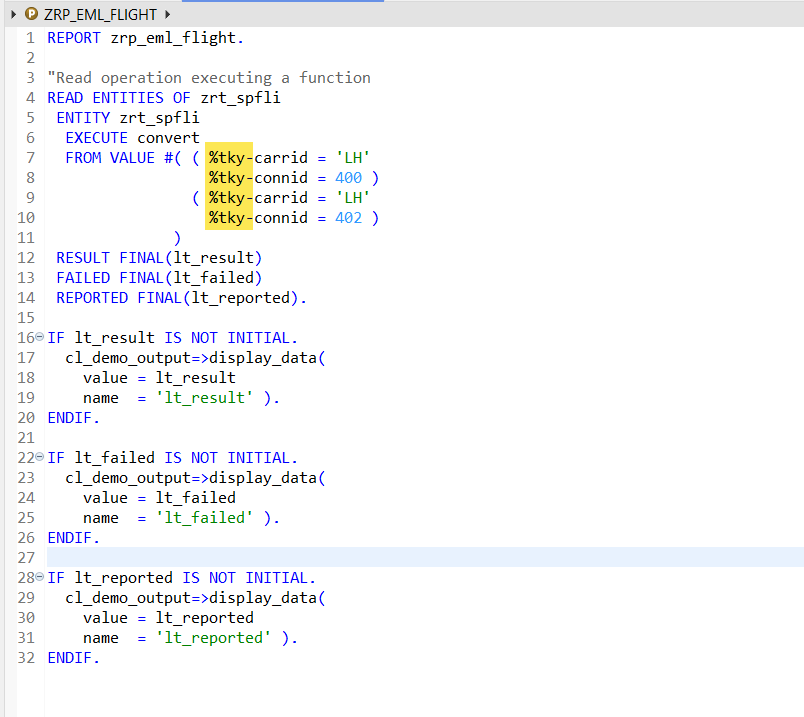
Try with multiple keys-
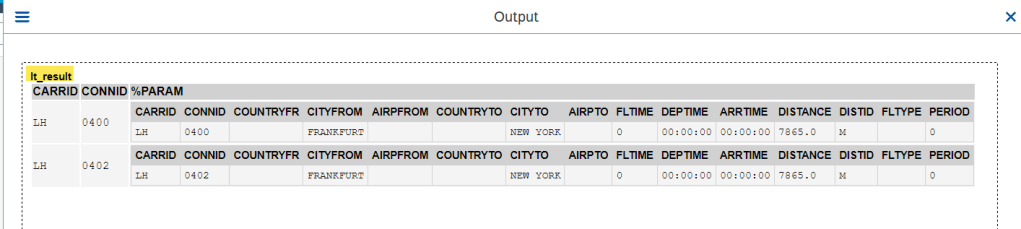
O/P-
Thanks it is useful, can you try similar examples with custom entity and how to read associate values from normal entity to custom entity
LikeLike